Windows Setup
PyVISA Windows installation - NI-VISA drivers, Python environments, corporate setups, troubleshooting, and configurations for instrument control.
PyVISA installation on Windows from basic setup to enterprise environments and troubleshooting.
Quick Start (5 Minutes)
For experienced developers who need PyVISA working fast:
# 1. Download NI-VISA from ni.com (registration required)
# 2. Install with default settings
# 3. Install PyVISA
pip install pyvisa psutil zeroconf
# 4. Test installation
python -c "import pyvisa; print(pyvisa.ResourceManager().list_resources())"Installation Guide
Download the NI-VISA Driver
Why NI-VISA? While other VISA implementations exist (Keysight, R&S), NI-VISA is the most widely supported and tested with PyVISA.
Registration is needed before download: NI registration page. Then download the NI Package Manager.
Alternative Download Options
- Direct NI-VISA Runtime: For automated deployments, download the standalone runtime
- Corporate Users: Contact your IT department - many have NI site licenses
- Offline Installations: Download the full offline installer for air-gapped systems
Install the NI-VISA Driver
Fast Startup
The installer will ask you to disable Windows Fast Startup.
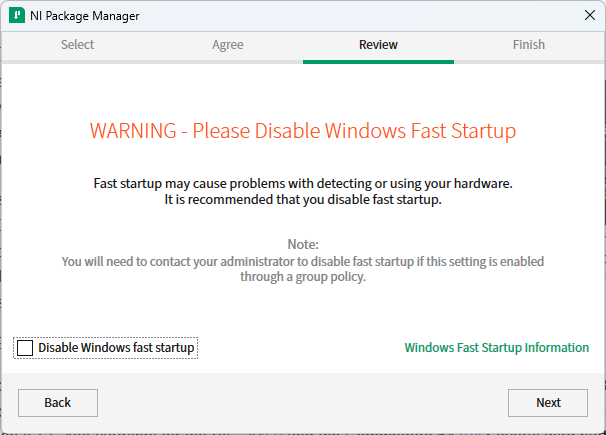
Fast Startup Consideration
On a development laptop, Fast Startup will likely not affect your setup. Fast Startup may prevent some interfaces from fully resetting, causing VISA to detect stale devices. On production machines, disabling Fast Startup is a good idea.
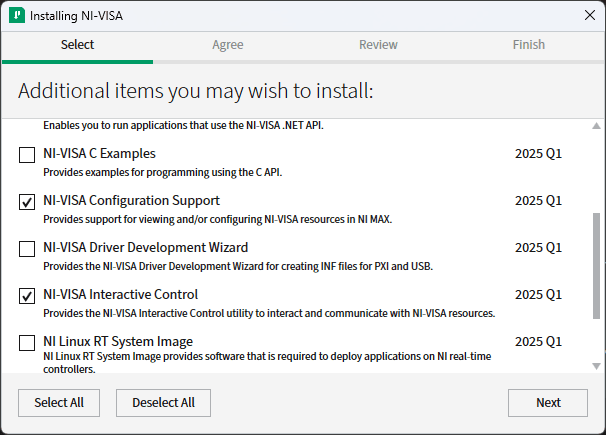
What to Install
After installing the NI Package Manager, it will ask what package you want.
For debugging and development, select:
- NI-VISA Configuration Support: For viewing/configuring instruments.
- NI-VISA Interactive Control: For testing VISA communication manually.
For production environments, uncheck everything and just click next. Only the VISA runtime is needed.
The VISA runtime is installed regardless of your selection. You will need to reboot after setup.
Installing PyVISA
PyVISA supports Python 3.6+. On Windows, Python is available via the Microsoft Store or can be installed from the official Python website.
Set Up a Virtual Environment (Optional, Recommended)
Get the virtualenv package from the command line:
pip install virtualenvThen navigate to your project folder and create the virtual environment:
python -m venv .venvYou will have to change the Windows script execution policy to be able to activate the virtual environment.
The safest way to do it would be:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy BypassHowever, it is not the most practical, you must run this command for each new terminal session.
Then enter the virtual environment:
.venv\Scripts\activateInstalling PyVISA
Now you can install PyVISA:
pip install pyvisaIf you are using a networked instrument, you will need:
pip install psutil zeroconfNow, open a Python interpreter:
pythonThen try:
import pyvisa
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
print(rm.list_resources())You should get output like this:
('ASRL3::INSTR', 'ASRL4::INSTR', 'USB0::VID::PID::SN::INSTR')In this case, the instrument is using USB.
Corporate and Enterprise Environments
Proxy and Firewall Configuration
Many corporate environments have network restrictions that affect PyVISA:
# For HTTP proxy environments
import os
os.environ['HTTP_PROXY'] = 'http://proxy.company.com:8080'
os.environ['HTTPS_PROXY'] = 'https://proxy.company.com:8080'
# Then install PyVISA
# pip install --proxy http://proxy.company.com:8080 pyvisaGroup Policy and Permissions
Corporate Windows machines often have restricted execution policies:
# Check current execution policy
Get-ExecutionPolicy
# For corporate environments, use RemoteSigned
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUserSilent Installation for IT Deployment
For automated deployments across multiple machines:
@echo off
REM Silent NI-VISA installation
NIPackageManager.exe --accept-license --install-packages "ni-visa"
REM Silent Python + PyVISA installation
pip install --quiet --no-input pyvisa psutil zeroconfAdvanced Configuration
Multiple VISA Runtime Management
If you need to work with multiple VISA runtimes:
import pyvisa
# Use specific VISA runtime
rm_ni = pyvisa.ResourceManager("C:/Windows/System32/visa32.dll") # NI-VISA
rm_ks = pyvisa.ResourceManager("C:/Program Files/Keysight/IO Libraries Suite/bin/visa32.dll") # Keysight
# Compare available resources
ni_resources = rm_ni.list_resources()
ks_resources = rm_ks.list_resources()
print(f"NI-VISA found: {ni_resources}")
print(f"Keysight found: {ks_resources}")Performance Optimization
For high-performance applications:
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
chunk_size | Buffer size for data transfers in bytes | number | 20480 |
timeout | Operation timeout in milliseconds | number | 2000 |
termination | Line termination character | string | \n |
import pyvisa
# Optimize for speed
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
inst = rm.open_resource("USB0::0x1234::0x5678::SN::INSTR")
# Increase buffer sizes for large data transfers
inst.chunk_size = 1024 * 1024 # 1MB chunks
inst.timeout = 30000 # 30 second timeout for large transfers
# Use binary transfers when possible
data = inst.query_binary_values("CURVE?", datatype='f')Virtual Machine and WSL Considerations
VMware/VirtualBox:
- Enable USB passthrough for USB instruments
- Allocate sufficient memory (minimum 4GB recommended)
- Install VMware Tools or VirtualBox Guest Additions
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL):
# PyVISA doesn't work directly in WSL
# Use Windows Python with PyVISA instead:
/mnt/c/Python39/python.exe -c "import pyvisa; print('Works!')"Comprehensive Troubleshooting
Device Not Found Issues
Step 1: Verify Physical Connection
import pyvisa
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
resources = rm.list_resources()
print(f"Found devices: {resources}")
# If empty, the issue is driver or hardware relatedStep 2: Check Windows Device Manager
- Open Device Manager (devmgmt.msc)
- Look for unknown devices under "Other devices"
- Check "Ports (COM & LPT)" for serial devices
- Verify "Universal Serial Bus controllers" for USB devices
Step 3: VISA Interactive Control Test
- Open NI-VISA Interactive Control (if installed)
- Try to connect to your device manually
- If this fails, the issue is hardware/driver related
Common Error Messages and Solutions
Driver Conflict Resolution
Identify Conflicting Drivers:
# Check installed VISA versions
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\Installer\Products" /s | findstr "VISA"Safe Driver Uninstallation Order:
- Uninstall manufacturer-specific VISA (Keysight, R&S, etc.)
- Uninstall old NI-VISA versions
- Clean registry entries
- Restart computer
- Install latest NI-VISA clean
Network Instrument Issues
Ethernet/TCP-IP Troubleshooting:
import pyvisa
import socket
# Test basic network connectivity first
def test_network_connection(ip, port=5025):
try:
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.settimeout(5)
result = sock.connect_ex((ip, port))
sock.close()
return result == 0
except:
return False
ip = "192.168.1.100"
if test_network_connection(ip):
print(f"Network connectivity to {ip} OK")
# Try PyVISA connection
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
try:
inst = rm.open_resource(f"TCPIP0::{ip}::5025::SOCKET")
print("PyVISA connection successful")
except Exception as e:
print(f"PyVISA connection failed: {e}")
else:
print(f"No network connectivity to {ip}")Common Firewall Ports:
- VXI-11: TCP 111 (portmap) and dynamic ports
- HiSLIP: TCP 4880
- Raw Socket: Custom port (often 5025, 5024)
- Telnet: TCP 23
Performance Troubleshooting
Slow Data Transfer:
import pyvisa
import time
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
inst = rm.open_resource("USB0::0x1234::0x5678::SN::INSTR")
# Benchmark data transfer
start_time = time.time()
data = inst.query_binary_values("CURVE?")
transfer_time = time.time() - start_time
data_size_mb = len(data) * 4 / 1024 / 1024 # Assuming 4-byte floats
transfer_rate = data_size_mb / transfer_time
print(f"Transferred {data_size_mb:.2f} MB in {transfer_time:.2f}s")
print(f"Transfer rate: {transfer_rate:.2f} MB/s")
# Optimize for better performance
inst.chunk_size = 1024 * 1024 # Increase chunk sizeDevelopment Best Practices
Proper Resource Management
import pyvisa
# Always use context managers for automatic cleanup
with pyvisa.ResourceManager() as rm:
with rm.open_resource("USB0::0x1234::0x5678::SN::INSTR") as inst:
# Your instrument code here
response = inst.query("*IDN?")
print(response)
# Resources are automatically closedError Handling Patterns
import pyvisa
from pyvisa import VisaIOError
def robust_instrument_communication():
try:
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
inst = rm.open_resource("USB0::0x1234::0x5678::SN::INSTR")
# Set up instrument parameters
inst.timeout = 5000
inst.write_termination = '\n'
inst.read_termination = '\n'
# Perform operations
idn = inst.query("*IDN?")
return idn.strip()
except VisaIOError as e:
print(f"VISA Error: {e}")
if e.error_code == -1073807339: # Timeout
print("Device is not responding - check connections")
elif e.error_code == -1073807343: # Invalid resource
print("Device not found - check resource string")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"Unexpected error: {e}")
return None
finally:
try:
inst.close()
rm.close()
except:
passLogging and Debugging
import pyvisa
import logging
# Enable PyVISA logging for debugging
pyvisa.log_to_screen(logging.DEBUG)
# Or log to file
logging.basicConfig(
filename='pyvisa_debug.log',
level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
)
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
inst = rm.open_resource("USB0::0x1234::0x5678::SN::INSTR")
# All VISA calls will now be logged
inst.write("*IDN?")
response = inst.read()Next Steps
Once PyVISA is installed and working:
- Learn interface specifics: Visit our Interface Configuration Guide
- Try examples: Start with our Oscilloscope Example
- Explore advanced features: Check out Performance Optimization
- Get help: Visit our Troubleshooting Hub
Alternative VISA Implementations
While NI-VISA is recommended, alternatives exist:
Keysight IO Libraries Suite
- Better performance with Keysight instruments
- Includes additional utilities and drivers
- Free download from Keysight website
PyVISA-py (Pure Python)
# No VISA runtime required
pip install pyvisa-py
# Use with PyVISA
python -c "import pyvisa; rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager('@py'); print(rm.list_resources())"R&S VISA
- Optimized for Rohde & Schwarz instruments
- Includes R&S-specific extensions
- Download from R&S support portal
How is this guide?